7D BIM Services (Project Lifecycle Information)
7D-BIM (seventh-dimensional building
information modelling) is used by managers in the
operation and maintenance of the facility throughout
its life cycle. The seventh dimension of BIM allows
participants to extract and track relevant asset data
such as component status, specifications,
maintenance/ operation manuals, warranty data etc.
The utilization of 7D-BIM technology can
result in easier and quicker parts replacements,
optimized compliance and a streamlined asset life
cycle management over time. 7D BIM provides
processes for managing subcontractor/supplier data and facility component through the entire facility life cycle.
Sometimes referred to as integrated BIM or iBIM, 7D BIM involves the inclusion of information to support facilities
management and operation to drive better business outcomes. This data includes information on the manufacturer of a
component, its installation date, required maintenance, details of how the item should be configured, operated for optimal
performance, energy performance, along with lifespan and decommissioning data.
Adding this kind of detail to your information model allows decisions to be made during the design process - a boiler with
a lifespan of 5 years could be substituted with one expected to last 10, for example, if it makes economic or operational sense to
do so. In effect, designers can explore a whole range of permutations across the lifecycle of a built assets and quickly get an
understanding of impacts including costs. However, it is at handover, that this kind of information really adds value as it is passed
on to the end-user.
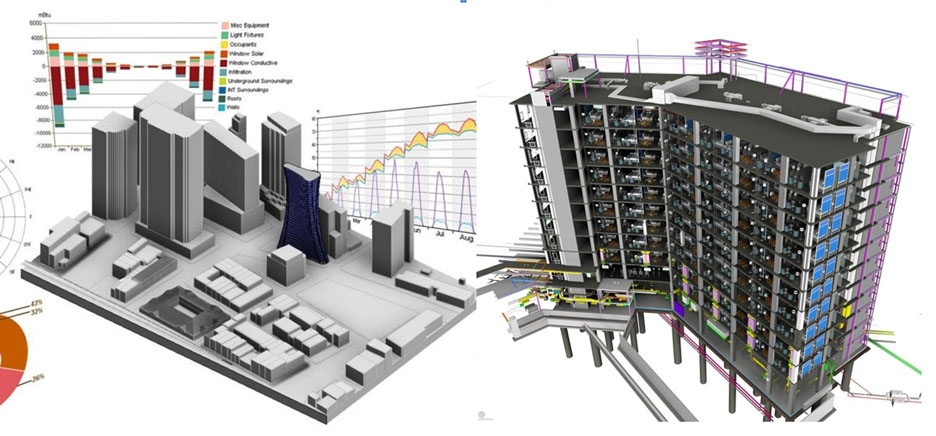
A model offers an easily-accessible and understood way of
extrapolating information. Details that would have been hidden in
paper files are now easily interrogated graphically. Where this
approach really comes into its own is in allowing facilities managers
to pre-plan maintenance activities potentially years in advance and
develop spending profiles over the lifetime of a built asset, working
out when repairs become uneconomical or existing systems
inefficient.
This planned and pro-active approach offers significant
benefits over a more reactive one - not least in terms of costs. Ideally
the information model should continue to develop during the in Use
phase with updates on repairs and replacements added in. Better
yet, a myriad of operational data and diagnostics can also be fed in
to inform decision making still further.

